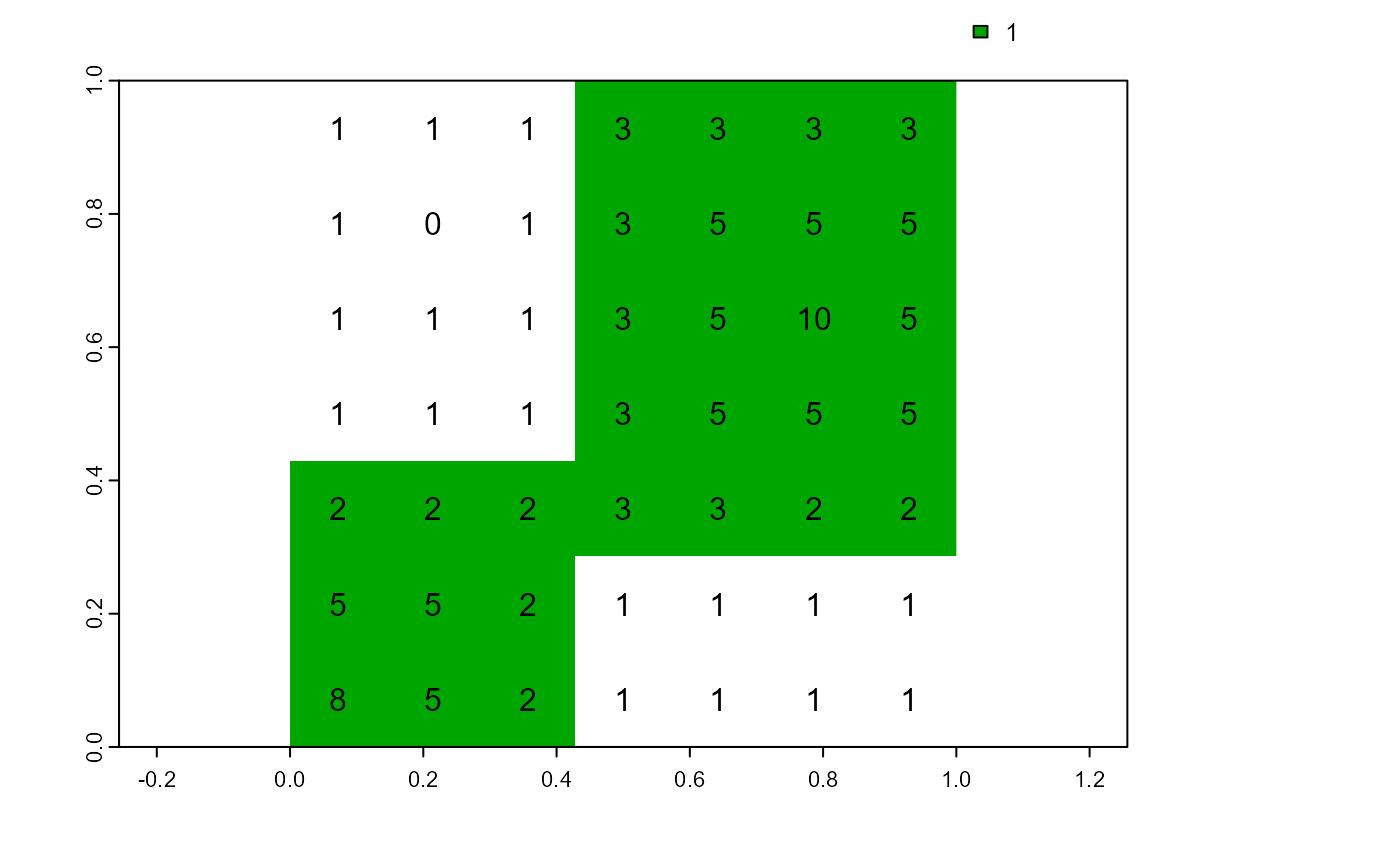
Transform a class vector or a generic vector into a raster.
cv.2.rast(
r,
classVector,
index = NULL,
plot = FALSE,
type = "classes",
writeRaster = NULL,
overWrite = FALSE
)Arguments
- r
raster object.
- classVector
numeric vector, the values to be assigned to the cell numbers indicated by
index.- index
numeric vector, the cell numbers of the argument
rto which assign the values of the argumentclassVector. IfNULL, the columnCellof the attribute tableattTbl(r)is used (seeattTbl).- plot
logic, plot the raster.
- type
character, type of map/legend. One of "continuous", "classes", or "interval".
- writeRaster
filename, if a raster name is provided save the raster to a file.
- overWrite
logic, if the raster names already exist, the existing file is overwritten.
Value
A class vector or a generic vector transformed into a raster.
Details
The arguments index and vector need to have the same
length. The function assign the values of vector at the positions of
index to an empty raster having the same spatial properties of the
raster r.
Examples
library(scapesClassification)
library(terra)
# LOAD THE DUMMY RASTER
r <- list.files(system.file("extdata", package = "scapesClassification"),
pattern = "dummy_raster\\.tif", full.names = TRUE)
r <- terra::rast(r)
# COMPUTE THE ATTRIBUTE TABLE
at <- attTbl(r, "dummy_var")
# COMPUTE THE LIST OF NEIGBORHOODS
nbs <- ngbList(r)
# Compute an example class vector
cv <- cond.4.all(attTbl = at, cond = "dummy_var > 1", class = 1)
# Class vector to raster
cv.2.rast(r, cv, plot = TRUE)
#> class : SpatRaster
#> dimensions : 7, 7, 1 (nrow, ncol, nlyr)
#> resolution : 0.1428571, 0.1428571 (x, y)
#> extent : 0, 1, 0, 1 (xmin, xmax, ymin, ymax)
#> coord. ref. : lon/lat WGS 84 (EPSG:4326)
#> source : memory
#> name : dummy_raster
#> min value : TRUE
#> max value : TRUE
text(r) # add raster values